https://vjudge.net/problem/UVA-548
题意:给一棵树的中序和后序遍历 找一个叶子使它到根路径上的权合最小
呜呜呜。。。终于要面对一直学不会的东西了
思路:递归思想 后序遍历最后遍历的一定是根结点 因此可以在中序遍历中找到左右子树 之后我们可以从左子树的部分那些节点中 从后序遍历中找他们的根节点 之后不断地便利下去 找权合最小的 再遍历一边 这个不是重点 我们拿样例来摸你一下这个神奇的过程
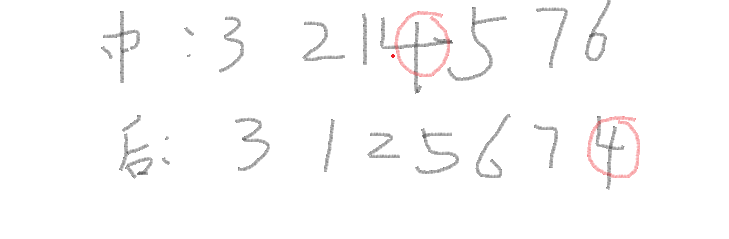
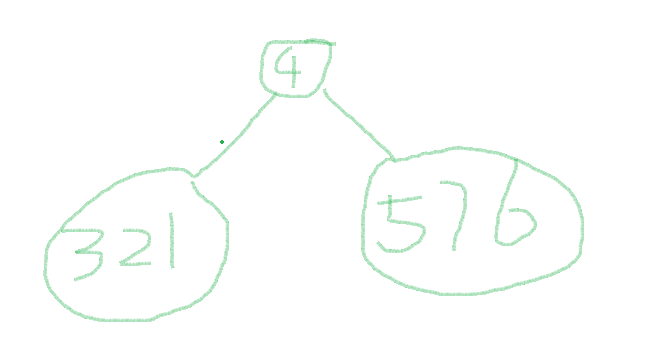
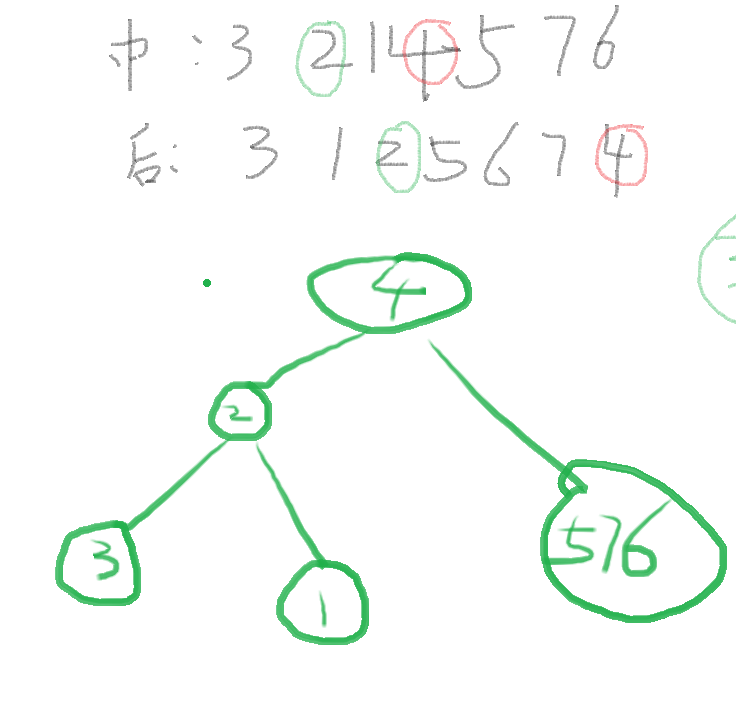

#include<algorithm>
#include<iostream>
#include<vector>
#include<cstdio>
#include<cstring>
#include<cmath>
#include<string>
#include<ctime>
#include<map>
#include<stack>
#include<set>
#include<cstring>
#include<sstream>
#include<queue>
using namespace std;
const int maxn = 10005;
int in_order[maxn], post_order[maxn], lch[maxn], rch[maxn];
int n;
bool read_list(int* a) {
string line;
if (!getline(cin, line)) return false;
stringstream ss(line);
n = 0;
int x;
while (ss >> x) {
a[n++] = x;
}
return n > 0;
}
int build(int L1, int R1, int L2, int R2) {//L1 R1对应中序序列 L2 R2对应后序序列
//cout << L1 << ' ' << R1 << ' ' << L2 << ' ' << R2 << endl;
if (L1 > R1) return 0;
int root = post_order[R2];//后序遍历的最后一个节点
int p = L1;//从中序的第一个节点开始找
while (in_order[p] != root)
p++;//找到那个对应的根节点
int cnt = p - L1;//左子树的节点个数
lch[root] = build(L1, p - 1, L2, L2 + cnt - 1);//左孩子 从对应左部分
rch[root] = build(p + 1, R1, L2 + cnt, R2 - 1);//右子树 对应右部分 中序遍历少了中间那个点 后序遍历少了最后面那个点
return root;
}
int best, best_num;
void dfs(int u, int sum) {
sum += u;
if (!lch[u] && !rch[u]) {
if (sum < best_num || (sum == best_num && u < best)) {
best = u;
best_num = sum;
}
}
if (lch[u]) dfs(lch[u], sum);
if (rch[u]) dfs(rch[u], sum);
}
int main() {
while (read_list(in_order)) {
read_list(post_order);
build(0, n - 1, 0, n - 1);
best_num = 0x3f3f3f3f;
dfs(post_order[n - 1], 0);//根节点
cout << best << endl;
}
return 0;
}










Comments | NOTHING