http://poj.org/problem?id=3070
Fibonacci可谓是一个陪伴我很多年的问题了 我们知道 数组开不到1e9那么大 那么我们如何算Fibonacci数列的第999999999项呢 在学习了矩阵快速幂之后 我得到了一个递推式 感觉真的是好神奇的东西
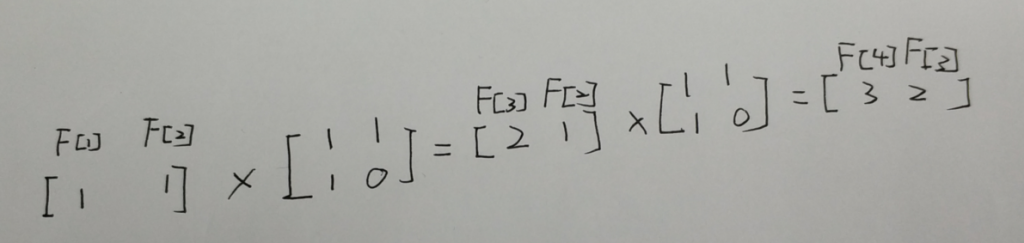
也就是说我们构造两个矩阵 第一个矩阵1*2 第二个矩阵2*2 由图我们可以得知 1*2的矩阵*上第二个矩阵的n次后 得到的矩阵中[0][0]元素就是Fibonacci数列的第n项
因此 我们可以快速计算Fibonacci数列的高次项
#include <set>
#include<iostream>
#include <cstdio>
#include <algorithm>
#include<string>
#include<cstring>
using namespace std;
const int maxn = 4;
const int mod = 10000;
typedef long long ll;
struct mat {
ll m[maxn][maxn];
mat() {
memset(m, 0, sizeof(m));
}
}unit;
mat operator *(mat a, mat b) {
mat ret;
ll x;
for (int i = 0; i < maxn; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < maxn; j++) {
x = 0;
for (int k = 0; k < maxn; k++) {
x += ((ll)a.m[i][k] * b.m[k][j]) % mod;
}
ret.m[i][j] = x % mod;
}
}
return ret;
}
void init_nuit() {
for (ll i = 0; i < maxn; i++) {
unit.m[i][i] = 1;
}
return;
}
mat pow_mat(mat a, ll n) {
mat ret = unit;
while (n) {
if (n & 1) {
ret = ret * a;
}
a = a * a;
n >>= 1;
}
return ret;
}
int main() {
ios::sync_with_stdio(0);
cin.tie(0);
init_nuit();
int n;
mat a;
a.m[0][0] = 1;
a.m[0][0] = 1;
mat b;
b.m[0][0] = 1;
b.m[0][1] = 1;
b.m[1][0] = 1;
b.m[1][1] = 0;
//mat c = a * b;
//cout << c.m[0][0];
while (cin >> n) {
if (n == -1) break;
if (n == 0)puts("0");
else if (n == 1 || n == 2) puts("1");
else {
mat c = pow_mat(b, n-1);
mat d = a * c;
cout << d.m[0][0] % mod << endl;
}
}
return 0;
}










Comments | NOTHING